MITOCHONDRIA & MUSCLE
Optimal heart health depends on a pet’s overall health status. Maintaining dogs and cats in ideal body condition is fundamental to their well-being. Including a nutritional assessment during every veterinary exam can help pet owners meet this health goal for their pets.
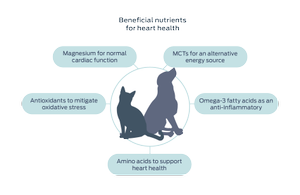
For heart-focused health, nutrition can play a key role in supporting cardiac function.
Read more to learn how specific nutrients can positively impact heart health.
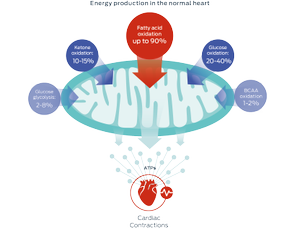
Adapted from Lopaschuk et al., 2010 & 2017
Fatty acids
These nutrients are the primary substrate used by mitochondria to generate energy for the heart, in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
However, mitochondria are also metabolically flexible – they can use different substrates to adapt to nutrient availability, changing cardiac workloads, or altered metabolic conditions. Other energy sources include glucose, ketones, and branched chain amino acids (BCAA).1–3

Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs)
MCTs provide a source of medium-chain fatty acids (MCFAs). With shorter carbon chains, MCFAs do not require transporters for uptake into mitochondria. With fewer metabolic steps involved, MCFAs are more rapidly oxidized into energy.4
Studies have also shown that MCTs can reduce mitochondrial and cytoplasmic reactive oxygen species which has a favorable impact on cardiac disease progression.5–8

Omega-3 fatty acids
Research shows that long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, especially eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), have numerous cardiac benefits: they help reduce inflammatory mediators and oxidative stress, stabilize cardiac arrhythmias in dogs, reduce blood pressure, and reduce cardiac remodeling in heart disease.9–17
Cardiac cachexia is common in dogs with congestive heart failure, and loss of lean body mass is associated with significantly shorter survival times.18–19 Inflammation appears to be causative or contributory for cachexia. Thus, another benefit of omega-3s may be decreased adverse effects from inflammation on lean body mass.20–22
Amino acids: taurine, lysine and methionine
Taurine is the most abundant amino acid in heart tissue. While its exact role is not yet known, studies show taurine is important for maintaining heart muscle contractility and homeostasis.23–25 In cats, taurine is an essential amino acid, however, taurine deficiency can lead to myocardial failure in both dogs and cats.26
Lysine and methionine are amino acid precursors for the synthesis of carnitine, a peptide which helps transport long-chain fatty acids into mitochondria for ATP production.27

Vitamin E
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are a result of cell metabolism. However, if ROS accumulate, then oxidative stress increases, leading to cell membrane damage, DNA damage and protein denaturation. Excess ROS can also trigger a cascade of molecular events that contribute to heart disease. Vitamin E is a cellular antioxidant that scavenges ROS and prevents damage from oxidative stress.
Under conditions of mitochondrial dysfunction – which contributes to heart failure – ROS levels increase, raising the need for antioxidants.28–32

Magnesium
Magnesium has multiple roles in maintaining healthy heart function, including antiarrhythmic and antioxidant actions. In heart cells, this mineral also helps transport ATP. In people, inadequate levels of magnesium correlate with heart failure and increased risk for cardiovascular disorders.33–36
Purina's research

Aging hearts do not adapt to disease or environmental changes as well as younger hearts. Studies have shown that increases in a particular molecular cascade, called the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway, are among the many changes associated with accelerated aging.37–39
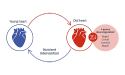
Purina scientists mined publicly available gene expression data of aging hearts.40, 41
This computational approach revealed that four genes for the Wnt signaling pathway were downregulated in older hearts.
However, dietary intervention with caloric restriction or supplementation with the antioxidant resveratrol restored gene expressions to the levels seen in young hearts.42–43
This research showed how nutrition could positively affect heart aging at the molecular level, which led to studies exploring ways that specific nutrients could support or improve cardiac function.
Key things to remember
- Many nutrients have recognized benefits for heart health.
- Fatty acids are the primary source of ATP generated by cardiac mitochondria.
- Purina’s computational study shows how nutrition can have positive impacts on heart aging.
Explore areas of transforming heart health:
Find out more
- Doenst, T., Nguyen, T. D., & Abel, E. D. (2013). Cardiac metabolism in heart failure: implications beyond ATP production. Circulation Research, 113(6), 709–724.
- Lopaschuk, G.D., Ussher, J.R., Folmes, C.D., Jaswal, J.S., & Stanley, W.C. (2010). Myocardial fatty acid metabolism in health and disease. Physiological Reviews, 90(1), 207–258.
- Lopaschuk, G. (2017). Metabolic Modulators in Heart Disease: Past, Present, and Future. Canadian Journal of Cardiology, 33, 838–849.
- Labarthe, F., Gélinas, R., & Des Rosiers, C. (2008). Medium-chain fatty acids as metabolic therapy in cardiac disease. Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy, 22(2), 97–106.
- Bach, A.C., & Babayan, V.K. (1982). Medium-chain triglycerides: an update. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 36(5), 950–962.
- Finck, B. N., Han, X., Courtois, M., Aimond, F., Nerbonne, J. M., Kovacs, A., Gross, R. W., & Kelly, D. P. (2003). A critical role for PPARalpha-mediated lipotoxicity in the pathogenesis of diabetic cardiomyopathy: modulation by dietary fat content. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100(3), 1226–1231.
- Labarthe, F., Khairallah, M., Bouchard, B., Stanley, W.C., & Des Rosiers, C. (2005). Fatty acid oxidation and its impact on response of spontaneously hypertensive rat hearts to an adrenergic stress: benefits of a medium-chain fatty acid. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 288(3), H1425–36.
- Saifudeen, I., Subhadra, L., Konnottil, R., & Nair, R. R. (2017). Metabolic Modulation by Medium-Chain Triglycerides Reduces Oxidative Stress and Ameliorates CD36-Mediated Cardiac Remodeling in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat in the Initial and Established Stages of Hypertrophy. Journal of Cardiac Failure, 23(3), 240–251.
- Bauer, J.E. (2006). Metabolic basis for the essential nature of fatty acids and the unique dietary fatty acid requirements of cats. Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association, 229(11), 1729–1732.
- Billman, G.E., Kang, J.X., & Leaf, A. (1999). Prevention of sudden cardiac death by dietary pure omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in dogs. Circulation
,99(18), 2452–2457. - Freeman, L.M., Rush, J.E., Kehayias, J.J., Ross, J.N. Jr, Meydani, S.N., Brown, D.J., … Roubenoff, R. (1998). Nutritional alterations and the effect of fish oil supplementation in dogs with heart failure. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 12(6), 440–448.
- Freeman, L.M. (2010). Beneficial effects of omega-3 fatty acids in cardiovascular disease. Journal of Small Animal Practice, 51(9), 462–470.
- Laurent, G., Moe, G., Hu, X., Holub, B., Leong-Poi, H., Trogadis, J., Connelly, K., Courtman, D., Strauss, B. H., & Dorian, P. (2008). Long chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids reduce atrial vulnerability in a novel canine pacing model. Cardiovascular Research, 77(1), 89–97.
- London, B., Albert, C., Anderson, M. E., Giles, W. R., Van Wagoner, D. R., Balk, E., … Lathrop, D. A. (2007). Omega-3 fatty acids and cardiac arrhythmias: prior studies and recommendations for future research: a report from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and Office Of Dietary Supplements Omega-3 Fatty Acids and their Role in Cardiac Arrhythmogenesis Workshop. Circulation, 116(10), e320–e335.
- Smith, C.E., Freeman, L.M., Rush, J.E., Cunningham, S.M., & Biourge, V. (2007). Omega-3 fatty acids in Boxer dogs with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 21(2), 265–273.
- Wall, R., Ross, R. P., Fitzgerald, G. F., & Stanton, C. (2010). Fatty acids from fish: the anti-inflammatory potential of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids. Nutrition Reviews, 68(5), 280–289.
- Hansen, R. A., Ogilvie, G. K., Davenport, D. J., Gross, K. L., Walton, J. A., Richardson, K. L., Mallinckrodt, C. H., Hand, M. S., & Fettman, M. J. (1998). Duration of effects of dietary fish oil supplementation on serum eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid concentrations in dogs. American Journal of Veterinary Research, 59(7), 864–868.
- Ineson, D. L., Freeman, L. M., & Rush, J. E. (2019). Clinical and laboratory findings and survival time associated with cardiac cachexia in dogs with congestive heart failure. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 33(5), 1902–1908.
- Freeman, L.M. (2012). Cachexia and sarcopenia: emerging syndromes of importance in dogs and cats. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 26(1), 3–17.
- Dupont, J., Dedeyne, L., Dalle, S., Koppo, K., & Gielen, E. (2019). The role of omega-3 in the prevention and treatment of sarcopenia. Aging Clinical and Experimental Research, 31(6), 825–836.
- Gorjao, R., Dos Santos, C., Serdan, T., Diniz, V., Alba-Loureiro, T. C., Cury-Boaventura, M. F., Hatanaka, E., Levada-Pires, A. C., Sato, F. T., Pithon-Curi, T. C., Fernandes, L. C., Curi, R., & Hirabara, S. M. (2019). New insights on the regulation of cancer cachexia by N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 196, 117–134.
- Robinson, S. M., Reginster, J. Y., Rizzoli, R., Shaw, S. C., Kanis, J. A., Bautmans, I., … Cooper, C., & ESCEO working group (2018). Does nutrition play a role in the prevention and management of sarcopenia? Clinical Nutrition (Edinburgh, Scotland), 37(4), 1121–1132.
- Sanderson S. L. (2006). Taurine and carnitine in canine cardiomyopathy. The Veterinary Clinics of North America. Small Animal Practice, 36(6), 1325–viii.
- Schaffer, S., Solodushko, V., & Azuma, J. (2000). Taurine-deficient cardiomyopathy: role of phospholipids, calcium and osmotic stress. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 483, 57–69.
- Schaffer, S. W., Jong, C. J., Ramila, K. C., & Azuma, J. (2010). Physiological roles of taurine in heart and muscle. Journal of biomedical science, 17, Suppl 1(Suppl 1), S2.
- Pion, P.D., Kittleson, M.D., Rogers, Q.R., & Morris, J.G. (1987). Myocardial Failure in Cats Associated with Low Plasma Taurine: A Reversible Cardiomyopathy. Science, 237, 764–768.
- Wang, Z., Liu, Y., Liu, G., Lu, H., Mao, C. (2018). L-Carnitine and heart disease. Life Sciences, 184, 88-97.
- Birringer, M., & Lorkowski, S. (2019). Vitamin E: regulatory role of metabolites. International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Life, 71(4), 479–486.
- Michałek, M., Tabiś, A., Cepiel, A., & Noszczyk-Nowak, A. (2020). Antioxidative enzyme activity and total antioxidant capacity in serum of dogs with degenerative mitral valve disease. Canadian Journal of Veterinary Research, 84(1), 67–73.
- Pryor, W. A. (2000). Vitamin E and heart disease: basic science to clinical intervention trials. Free radical biology & medicine, 28(1), 141–164.
- Sagols, E., & Priymenko, N. (2011). Oxidative stress in dog with heart failure: the role of dietary fatty acids and antioxidants. Veterinary Medicine International, 2011, 180–206.
- Sozen, E., Demirel, T., & Ozer, N.K. (2019). Vitamin E: regulatory role in the cardiovascular system. International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Life, 71(4), 507–515.
- Del Gobbo, L.C., Imamura, F., Wu, J.H., de Oliveira Otto, M.C., Chiuve, S.E., & Mozaffarian, D. (2013). Circulating and dietary magnesium and risk of cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 98(1), 160–173.
- Freeman, L.M., Rush, J.E., & Markwell, P.J. (2006). Effects of dietary modification in dogs with early chronic valvular disease. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 20, 1116–1126.
- Qu, X., Jin, F., Hao, Y., Li, H., Tang, T., Wang, H., Yan, W., & Dai, K. (2013). Magnesium and the risk of cardiovascular events: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. PloS one, 8(3), e57720.
- Tardy, A.L., Pouteau, E., Marquez, D., Yilmaz, C., & Scholey, A. (2020). Vitamins and Minerals for Energy, Fatigue and Cognition: A Narrative Review of the Biochemical and Clinical Evidence. Nutrients, 12(1). pii: E228.
- Brack, A. S., Conboy, M. J., Roy, S., Lee, M., Kuo, C. J., Keller, C., & Rando, T. A. (2007). Increased Wnt signaling during aging alters muscle stem cell fate and increases fibrosis. Science (New York, N.Y.), 317(5839), 807–810.
- Liu, H., Fergusson, M. M., Castilho, R. M., Liu, J., Cao, L., Chen, J., … Finkel, T. (2007). Augmented Wnt signaling in a mammalian model of accelerated aging. Science (New York, N.Y.), 317(5839), 803–806.
- Marchand, A., Atassi, F., Gaaya, A., Leprince, P., Le Feuvre, C., Soubrier, F., Lompré, A. M., & Nadaud, S. (2011). The Wnt/beta-catenin pathway is activated during advanced arterial aging in humans. Aging Cell, 10(2), 220–232.
- Li, Q., & Hannah, S. S. (2012). Wnt/β-catenin signaling is downregulated but restored by nutrition interventions in the aged heart in mice. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics, 55(3), 749–754.
- Barger, J. L., Kayo, T., Vann, J. M., Arias, E. B., Wang, J., Hacker, T. A., Wang, Y., Raederstorff, D., … Prolla, T. A. (2008). A low dose of dietary resveratrol partially mimics caloric restriction and retards aging parameters in mice. PloS one, 3(6), e2264.